Evaluating the sustainability of Volgograd / N. Sadovnikova, D. Parygin, E. Gnedkova, B. Sanzhapov, N. Gidkova // The Sustainable City VIII : Proceedings of the Eight International Conference on Urban Regeneration and Sustainability, Section 3, Putrajaya, Malaysia, 3–5 December 2013. – WIT Press, 2013. – P. 279–290. – DOI : 10.2495/SC130241
Authors:
Danila Parygin
Natalia Sadovnikova
Elena Gnedkova
Bulat Sanzhapov
Nina Gidkova
Abstract
Accumulated industrial base of major Russian cities, carrying the burden of the economical transformations combined with the existing state-municipal management system, requires the determination of the effective ways to further improvement of the city analysis development plans.
The purpose of this study are the issues of assessing the sustainability of the city operation and development. The proposed approach allows us to evaluate current state and compare different scenarios.
For the formation the indicators state of the system we used H. Bossel methods. Identification of factors that need to be corrected was made on the basis of the «stars benchmarks». Analysis of factors that characterize the processes of change in the urban environment allows reasonably approach the process of selecting projects of development and transformation of the city.
This paper presents an approach to the analysis of scenarios for the city of Volgograd from the position of sustainable development. Using the methodology of cognitive modeling allows evaluating the effectiveness of decision-making and analyzing dynamics of situation when implementing the different scenarios.
On the basis of the study and the simulation results we have made proposals that improve the sustainability of the urban system. Set of activities oriented to the improving the subsystems of “local community”, “urban environment” and “life activity processes” should form factors of sustainable urban development.
Keywords: local community, urban environment, local self-government, life activity in a city, scenario forecasting, cognitive modeling, stars benchmarks, Volgograd, sustainable development
1 Introduction
Orientation on the service industry, transport and power units and other business objects becomes the inevitable consequence of the concept of physical planning major cities in Russia, since industrialization began. As a result we have a significant imbalance in the development of urban areas and the significant increase in anthropogenic pressure. To change the situation, in the first instance we need to review the criteria for assessing urban development and to form new territories planning principles, taking into account natural conditions and characteristics. This approach could allow more efficient use of existing resources and reduce the load on the environment.
The basic criteria for assessing the effectiveness of city development strategies are sustainable development indicators. Despite the dynamic evolution of the sustainable development theory, the problems of assessing the complex impact of economic activity and predict anthropogenic pressures are still sufficiently studied. First of all, little attention is paid to the prediction of the impact assessment carried out by urban policy and the study of synergistic and cumulative effects.
In the performance of a strategic planning and development of the city tasks it’s necessary to analyze the current situation and opportunities. This requires mechanisms to enable generate alternative scenarios to assess the effectiveness of decisions. This article discusses one of the approaches to the analysis of strategic development plans based on cognitive modeling and methodology developed by H. Bossel at the International Institute Sustainable Development.
2 Sustainability and sustainable development
The concept of sustainability has many interpretations and meanings [1-5]. A number of researchers link the sustainability to the nature of exposure-response [2]. There are approaches based on an assessment of the use of environmental resources effectiveness [3]. On another statement, sustainability means admissible measure deviations from the specified properties ecosystems norms. The deviation caused by some measure of external factors disturbance [4]. Another interpretation of the sustainability concept is associated with risk [5]: «for the sustainability of the system is meant to achieve a sufficiently low level of risk, estimated the value of potential losses related to decision-making with incomplete information».
The variety of definitions and forms of the sustainability concept presentation says that there is no unified methodology for evaluating this property. In practice, the most common conclusions on the stability of ecosystems are based on empirical research. Selection of estimated parameters is defined by targets and specific conditions of the problem being solved. Assessing the sustainability of urban ecosystem is even more difficult along with the assessment of complex natural relations you must take into account anthropogenic impact and the intrinsic properties of the technosphere.
Along with the concept of «sustainability urban ecosystem» there is the concept of «sustainable development». As in the case of the sustainability, a common approach to this problem does not exist so far. «Sustainable development» can be consumed to the entire planet as a whole, as well as relative to certain countries, regions, different types of business. A detailed theoretical and methodological analysis of the sustainable development problems are given in the work V. I. Danilov-Danil’yan [6]. In his view, sustainable development is «a social development that does not break down its natural foundation, created living conditions do not cause degradation of the human and socio-destructive processes do not develop to the scale of threats to public safety». A. A. Voronin [7] formulates the problem of sustainable development as «finding a balance between static and dynamic stability, i.e. rational degree of decentralization structure of the large open system, enabling its self-development and at the same time ensuring the integrity and security in a changing external environment». This interpretation correlates with Le Chatelier’s principle of sustainability, if we consider the «sustainable development» as a property, which can have the city as an open system. Practical advice on the selection of indicators and methods of the territories stability analysis are represented in the work of H. Bossel [8].
H. Bossel equates the concept of «system stability» and «sustainable development» [8]. At the same time the indicators should reflect the operation of the system and carry information about the system viability current state and system’s contribution to the functioning of its dependent systems.
We should use this method of the system description, when dealing with a large systems that characterized by a variety of indicators. Such indicators are often not lead to a single integral indicator, as most of them often are not additive and cannot be added.
According to Bossel’s approach. for any system you can distinguish six basic guidelines, caused by surroundings: existence, effectiveness, freedom of action, safety, adaptability and coexistence, as well as three basic guide, due to the system (inherent only self-reproducing system, endowed with consciousness and sensitivity): reproducibility, psychological needs and responsibility [8]. The system is stable with a balanced minimum satisfaction benchmarking. It should be noted that this approach is not possible to do without a large proportion of subjective information. But in spite of this, studies have confirmed that the selection of indicators, based on a baseline assessment of the stability of system, will have comparable results, even if the initial list of indicators will be completely different [9].
Based on the obtained values, you can build a «star benchmarks» for each subsystem [10]. Each «star benchmarks» reflects the stability of the subsystem. On each ray value variation of the subsystem indicators is separated off for the selected period. Relative values are calculated to bring to unified units of measurement (attitude indicator to its value in the previous period). The closer dots on the rays of the «stars» to 1, the more stable the system.
Factors that need to be adjusted are displayed on the «star» in the form of «failures». Change of these indicators will bring the system to more sustainable position. By selecting different combinations of manage impacts you can track the dynamics of development system, depending on the chosen scenario. You can identify the best scenario possible by analyzing area and form of built «stars». Quantitative assessment of the generalized criterion can be obtained based on the principle of maximizing solution in task with fuzzy goals and fuzzy constraints [11].
In order to quantify the construction of scenarios of development, we introduce the concept coefficients of «area» and «shape». Comparing these coefficients, we can estimate how effective a particular scenario and choose the most favorable on the basis which will be built in the future development strategy.
The coefficient of the star area (kS) is equal the ratio of the square of the star to the area of the star with the maximum viability:
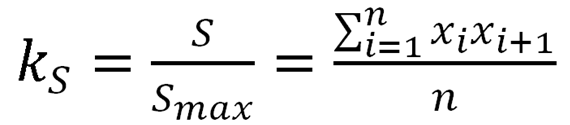
Area coefficient assumes values [0,1]. kS = 1 corresponds to a system with a maximum viability, and kS = 0 – the system with a minimum viability.
Shape coefficient (kf) expresses the deviation of the resulting star shape from the star of correct form (shape of a regular polygon), i.e. of the star, which has an equal value of the vector of baseline.
The formula to calculate the shape coefficient is proposed:
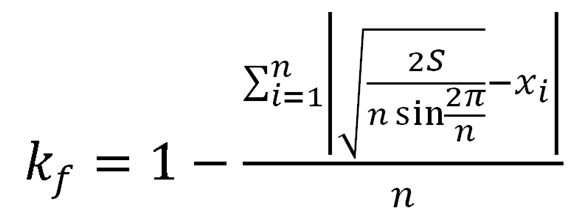
The shape factor takes values [0,1]. kf = 1 corresponds to a system having the most balanced development, i.e. development of the system across all baselines are equal, and kf = 0 is in accord with the system having unbalanced development.
Thus, we can conclude that the area coefficient shows how the system is close to the system with maximum viability. And the shape coefficient shows how the development of the system is balanced, i.e. how evenly system develops for a baseline.
3 Scenario forecasting
Classical methods of forecasting are focusing on assessing the most likely scenario of the system evolution. Scenario forecasting based on the view of the uncertainty and ambiguity of the trajectory of this development. Scenario forecasting allows the simultaneous consider several options for the development of the situation, analyzes the opportunities and risks.
The scenario approach does not specify the certain set of actions to establish forecast and defines a set of diverse techniques, methods, and mechanisms that allow synthesizing scenarios. One of the main tasks of scenario forecasting is to detect such factors laid in the current circumstances and situations that would create a mechanism for influencing the future state of the system. Identification of possible development scenarios is based on the scenario modeling [11-14].
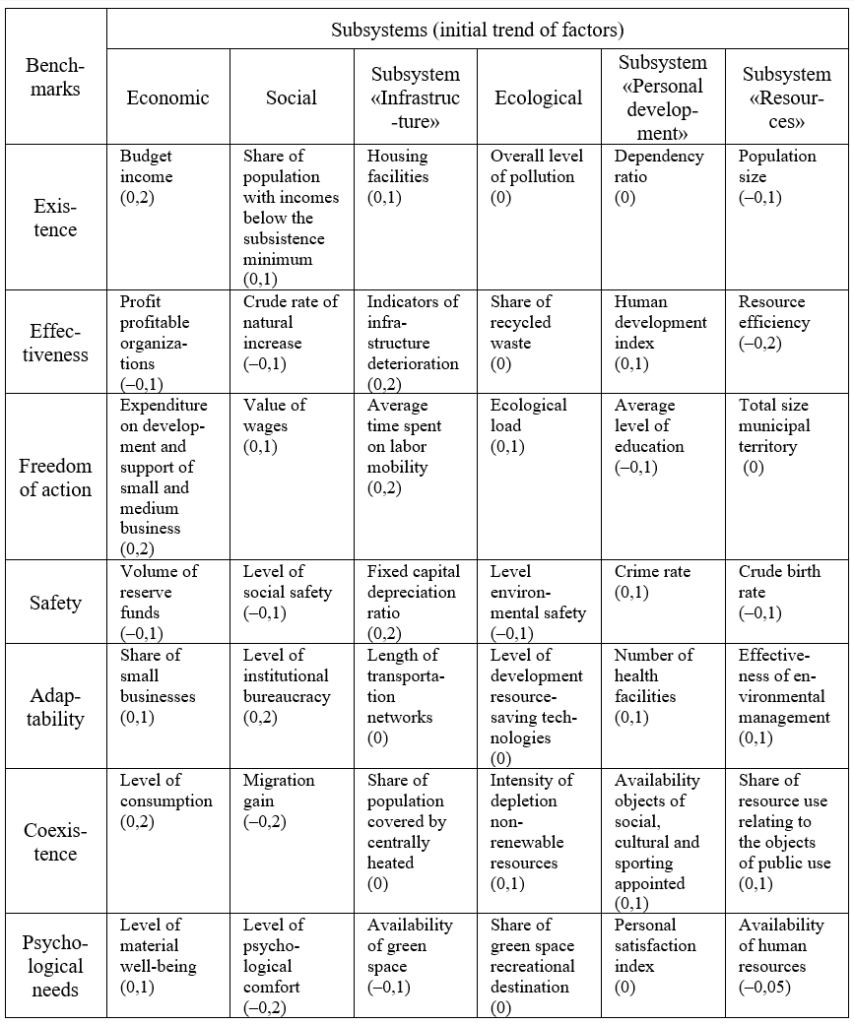
As background information for the model we used the official data of Federal Service of State Statistics of Russia, materials state report «On the state and environmental protection of the Russian Federation» in 2011, materials General development plan of the city of Volgograd, the strategic plan and the investment passport of Volgograd. Analysis was carried out on 42 factors, table 1. The initial trends were determined by statistical data 2008-2012.
Table 1: Benchmarks and indicators for sustainable development of Volgograd
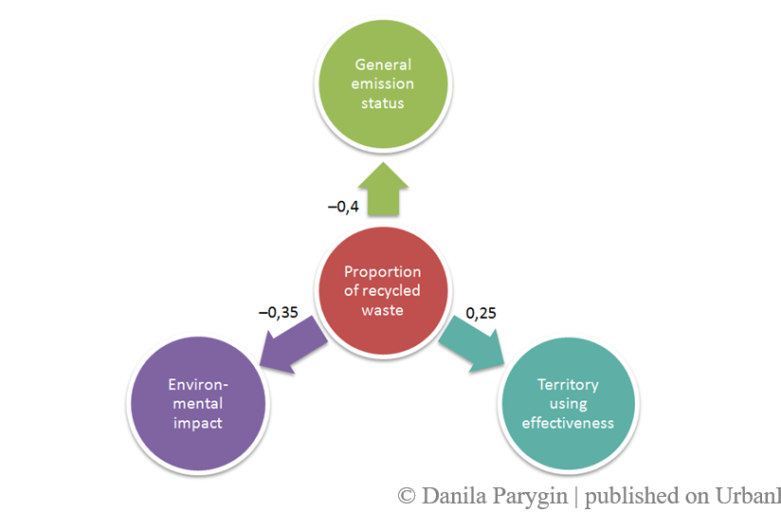
The model is defined as a directed graph of the sign in which the vertices are the factors of the situation, and the weighted arcs are cause-and-effect relationships, the weight of which reflects the strength of the influence factors of the situation, fig. 1. Directed graph defines the structure of the situation and formally represented as a directed graph G = {X, E}, which contains {X} – non-empty set of vertices (or indicators) and {E} – ordered set of arcs (positive or negative mutual influences). Map fragment in fig. 1 shows the principle of the model factors relations representation.
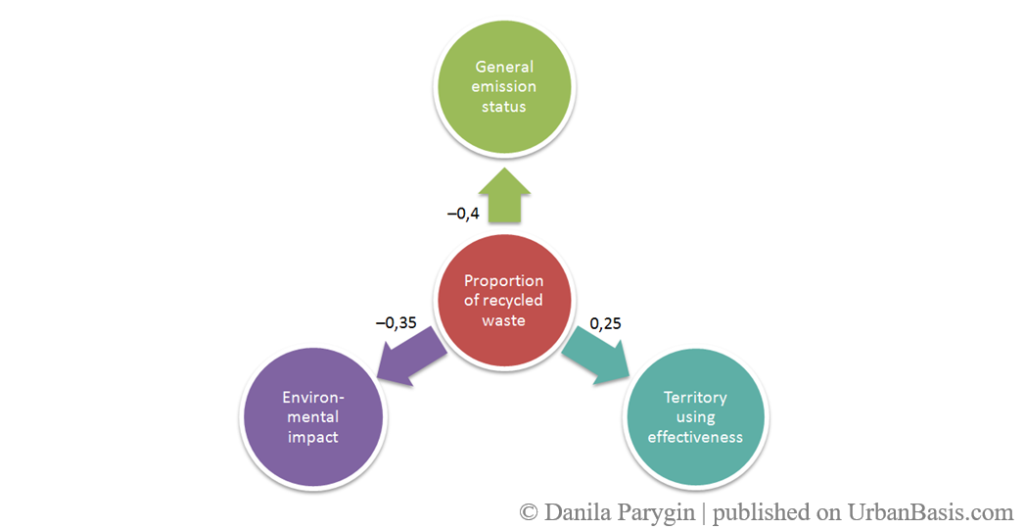
To construct the maps and implement procedures for cognitive analysis and scenario forecasting system we used «Strategist», developed at the Department of CAD, VSTU [15]. The system is designed to support management decision-making, identification and visual representation of expert knowledge of a subject domain, with the study and analysis of the complex semistructured systems functioning.
The value of «trend» factor in every moment is defined as the sum of the values of «trend» factor in the previous point, and all the influences that come from «neighboring» factors. Imitational experiments carried on the constructed model can identify the factors that cause marked changes observed factors that characterize the state of the city. Self-development situation implies the preservation of the initial trends. Managed development means targeting of one or more factors. Change of the current trend factor transmitted to other factors acts as the management [12].
For each of the five analyzed cities development scenarios have been determined the dynamics of change of each factor applied to assess the sustainability of the system. According to these data we built stars benchmarks, fig. 2.
According to the obtained stars benchmarks we calculated the coefficients of viability and balance the subsystems and the overall system, table 2. An integral indicator of sustainable development of the entire system was calculated as the average of the coefficients on all subsystems.
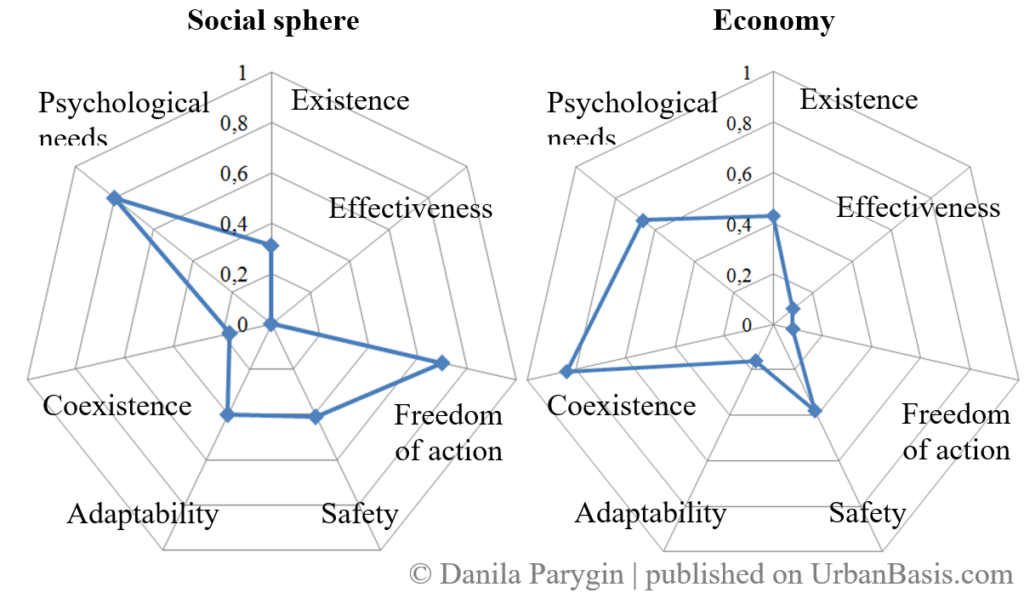
Table 2: The calculating results of the viability and balance coefficients
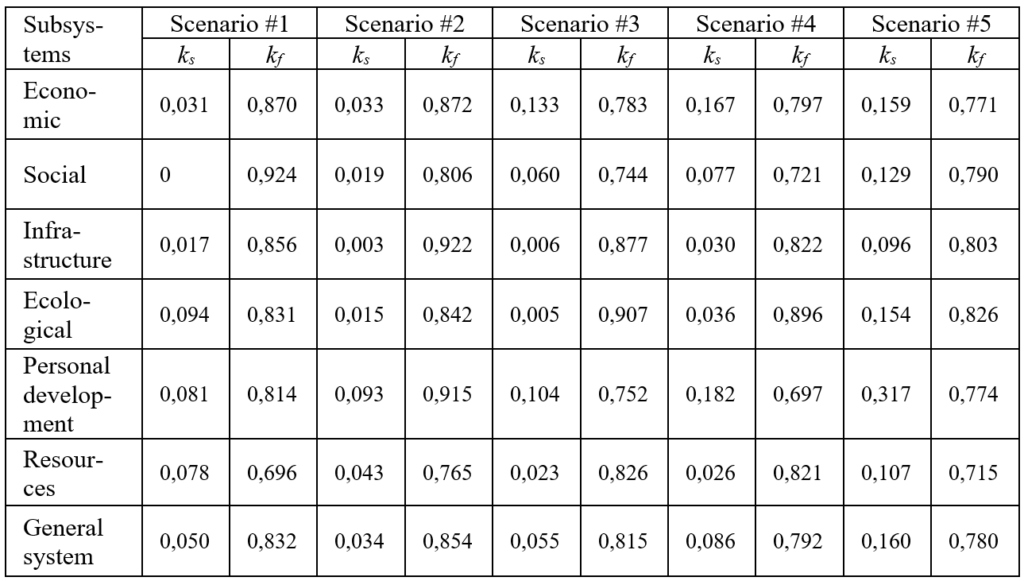
The most acceptable scenario is number 5. Corresponding to a given scenario, a set of manage impacts (table 3) can improve the viability and balance development all the subsystems. The main emphasis in the selection of activities to transform the urban environment associated with the intensification of the processes change of social and infrastructure indicators. Largest changes have to touch the higher standards of living, and especially wage increase (this indicator is one of the lowest in Russia).
Table 3: Manage factors for the chosen scenario
| Name of manage factor | Manage pulse |
| Volume of reserve funds | 0,35 |
| Value of wages | 0,70 |
| Indicators of infrastructure deterioration | –0,30 |
| Length of transportation networks | 0,60 |
| Level of development resource-saving technologies | 0,40 |
| Number of health facilities | 0,30 |
| Crime rate | –0,40 |
| Average level of education | 0,45 |
| Fixed capital depreciation ratio | –0,40 |
| Overall level of pollution | –0,40 |
| Share of resource use relating to the objects of public use | –0,50 |
| Level of institutional bureaucracy | –0,60 |
| Migration gain | 0,40 |
| Average time spent on labor mobility | –0,40 |
| Effectiveness of environmental management | 0,50 |
Achieving sustainable development requires a reliable system operation. But also we cannot just send all the resources to address the current problems. Elaboration of transparent and clear development program is an essential component of sustainable management of the city. In development plans of the city and the analysis of their implementation we should have the decisions assessment mechanism whereby you can predict the future state of the urban environment.
4 Activities to sustainable functioning
Based on these studies and modeling results the recommendations for changing the strategic development plan of the city were compiled. The authors identified three most significant at the moment areas:
1) local community development;
Volgograd, like many Russian cities, has a problem raising the importance of the processes taking place at the local level for the majority of residents in the consolidated purposes to achieve the desired changes. It’s necessary to promote the development of an active attitude to local issues. Activation of civic participation, increased citizen responsibility for the condition and development of the city, the analysis of social needs and their reflection in the strategic plans, the use of the intellectual potential of the residents are important to achieving the planned results in the implementation of development strategies.
A correlation between this principle and the forecast model estimates allows offering the following conclusions:
– value of wages – resource of time and effort valuable to a large extent determines the significance of human activity, self-esteem and social recognition – all these components are the factors of social stability;
– migration gain – sophisticated factor caused by proposal social and economic benefits offered by this area. For storing the positive potential of the city we should pay particular attention to the «quality» of migration – attracted labor and resettlement workers are guided in choosing the place as the level of wages in exchange for the qualification requirements and the state of the urban environment that accompanies the daily activities;
– average level of education – exceptional importance factor capable of stimulating constructive transformation at different levels of socio-economic interactions;
– opportunity to decrease the «crime rate» is connected with the creation of conditions for the harmonious development of man and the realization of his creative abilities. This requires, above all, increasing the importance of spiritual and cultural values, changing attitudes to education and forming a negative attitude to the «consumer society». Properly organized public space, combining the efforts of business and government to create new jobs and purposeful youth policy will not only reduce crime, but also enhance the attractiveness of the city;
– a high level of institutional bureaucracy provokes preservation imbalance in the distribution of money income and comes to be a deterrent to the development of self-government. In many countries there is a successful experience of replacement of obsolete forms of governance with the modern, based on the principles of transparency and citizen participation.
Recommendations to revitalize the local self-government can be summarized as follows:
– direct representation in the local self-government – there are objective ratio of effective representation by one person within a group of 5000 inhabitants (at this stage is exceeded six times);
– public control and supervisory commissions – the active involvement of inhabitants to work on projects of special relevance to specific community groups will raise awareness and involvement, as well as an interest in the successful implementation of the adopted development plans and programs;
– regular account of public opinion – range of opportunities to provide feedback to the process of transformation to date has grown significantly through the use of information and communication technologies – information about the needs can be obtained through the polls conducted in person or remotely, and indirectly in the processing of statistics regarding use of urban infrastructure and inhabitants interactions.
The practice of these tools will take root in their targeting of solving the problems of local importance. It is particularly important in the interaction organization of the local community to create conditions for the manifestation of the potential of innovative initiatives and the volunteer movement – many transformations simply do not disturb be implemented or put into the hands the tools and powers.
2) urban development;
Change in the physical space, which surrounds the human will transform the behavior and attitudes to what is happening. The city, like anthropogenic system must take into account the balance of the natural environment and economic activities, encouraging personal development of residents.
Group managing factors characterizing the quality of urban space includes: indicators of infrastructure deterioration; length of transportation networks; level of development resource-saving technologies; share of resource use relating to the objects of public use; number of health facilities; overall level of pollution; average time spent on labor mobility.
To improve the quality of the urban environment and the efficient use of city territory we need to:
– change approaches to the functional zoning of space. In the modern city the ways to implement all the needs of the residents should be optimized. In this regard, the conditions should be created to bring together within a block of office buildings, residential and sports facilities, shopping and cultural centers;
– allocate resources to enhance the comfort and reliability of public transport;
– restore the previous level of greening (in recent years it fell a few dozen times);
– create conditions for the development of IT-services for the identification of the preferences and needs of the inhabitants by taking into account the operational data collected by sensors, registrars, mobile devices. With the help of these technologies can be formed a unique database of static data, which, in contrast to the formal statistical surveys is always relevant and reflects the actual behavior of people, service users of the urban environment;
– purposefully form attitude to urban space as «my home». Create information services for the promotion of the ideas of improvement and restructuring of urban spaces.
3) system of city management optimization;
The market economy, international cooperation, the opening of new and new representatives of foreign commercial companies, all of this promotes penetration and diffusion in various socio-economic sectors of the system of city rules, requirements, practices and standards for different types of services. Meanwhile, there is still a strong tradition and preserved the structure of management of the urban system, the foundations of which were laid down and distributed throughout the country in the Soviet period.
Level of budgetary provision to a large extent defines the modern development and the potential of the largest cities in Russia, which are the municipalities in the federal subjects. In Volgograd, this rate is 10 times lower than in Moscow and two times lower than in Krasnodar.
Negative trends in indicators related to management efficiency above all related to a lack of funding, poor organization of personnel policy and non-systemic character of activities to transform the city. The optimal development indicators can only be achieved by adjustment of the existing administrative model.
Work performed by the administration and the provided services should be part of the urban service offering ensures the best solutions to tasks of life support of residents. In connection with this we propose:
– implement the procedure of alternative choice of service provider (development of competition and equal quality control of commercial, municipal and state services). This will offer the citizens the best ways to implement their demands and needs;
– accelerate the process of implementation of state-municipal services based on ICT. This will significantly reduce the corruption component and minimize administration costs;
– organizing permanent monitoring of the quality of services received by inhabitants;
– establish mechanisms for the implementation of ideas participatory governance based on ICT.
5 Conclusion
We chose the scenario approach due to the fact that the analysis of complex socio-economic systems has to deal with semi-structured and fuzzy data for the forecast of development.
We developed a system of indicators for sustainable development of Volgograd, based on the concept of a baseline system, which defines its basic properties. We developed an approach to the construction of a cognitive map development the territory, including the creation of a system of indicators for sustainable development of the territory and the definition of mutual influences a system factors.
We developed an approach to assessment of alternative development scenarios by building a «benchmarks stars» and the determination of the coefficients based on their vitality and balance. By using this approach constructed development scenarios of Volgograd was analyzed and we selected the best scenario for the realization of sustainable development.
For chosen scenario based on the input to the system managing factors and modeling results suggestions to improve the effectiveness of strategic management was made. Provide recommendations on reforms aimed at improving the functioning and development sub-systems of «local community», «urban environment» and «management processes».
Further research is focused on the development of the inventive methods and the creation of information analysis system to support decision-making in the field of urban planning project.
References
[1] Antonov, V.A. & Sidorova, A.E., Sustainability urboecosystems according to the theory auto-wave self-organization of active media. Ecology of Urbanized Areas, 4, pp. 14–21, 2006.
[2] Reimers, N.F., Ecology, Rossiya Molodaya: Moscow, pp. 165–192, 1994.
[3] Golubeva, E.I., Phitocenotic criteria for assessing the condition of ecosystems. Izvestiya VGO, 128(2), pp. 22–31, 1996.
[4] Levich, A.P., The concept of sustainability in biology. Mathematical Aspects. Man and Biosphere, 1, pp. 138–174, 1976.
[5] Zolotov, T.V. Models and risk management techniques and their application to environmental and economic systems, Abstract of doctoral thesis: Moscow, 2010.
[6] Danilov-Danil’yan, V.I., Sustainable development (theoretical and methodological analysis). Economics and Mathematical Methods, 39(2), pp. 17–34, 2003.
[7] Voronin, A.A., Sustainable development – a myth or a reality. Mathematical Education, 1, pp. 59–67, 2000.
[8] Bossel, H., Indicators of Sustainable Development: Theory, method, practical use. The report, submitted for consideration by Balaton Group, Publishing House IDN SB RAS: Tyumen, pp. 5–46, 2001.
[9] Semenova, T.Yu., Formation of a system of indicators for sustainable development of large city. Problems of a Modern Economy. Eurasian International Scientific Analytical Journal, 2(22), pp. 290–294, 2007.
[10] Sadovnikova, N.P., Application of the cognitive modeling for analysis of the ecological and economical efficiency of the urban planning project. Internet-vestnik VolgGASU. Civil Engineering Informatics, 5(14), pp. 1–7, 2011.
[11] Sanzhapov, B. & Sadovnikova, N.P., Agree objectives for environmental and economic feasibility of urban project subject to the restrictions on the values of the characteristics included in the system means in terms of fuzzy information. Vestnik VolgGASU. Construction and Architecture, 21(40), pp. 151–159, 2011.
[12] Sadovnikova, N.P., Parygin, D.S., Gnedkova, E.P., Kravets, A.G., Kizim, A.V. & Ukustov, S.S., Scenario forecasting of sustainable urban development based on cognitive model. ICT, Society and Human Beings 2013. Proceedings of the IADIS International Conference, IADIS Press: Prague, pp. 115–119, 2013.
[13] Parygin, D.S., Sadovnikova, N.P. & Gidkova, N.P., Constructing trajectories territorial development based on methods of scenario forecasting. Internet-vestnik VolgGASU. Construction Informatics, 8(24), pp. 1–9, 2012.
[14] Parygin, D.S., Assesment the effectiveness management strategies of urban area based on scenario models. Proceedings of Volgograd State Technical University. Actual problems of management, computer science and informatics in technical systems, 8(111), pp. 98–103, 2013.
[15] Zabolotskiy, M.A., Tikhonin, A.V. & Polyakov, I.A., Analytical software system “Strategist” – the tool of goal-setting and analysis of complex systems and situations. Proceedings of Volgograd State Technical University. Actual problems of management, computer science and informatics in technical systems, 2(4), pp. 65–68, 2008.